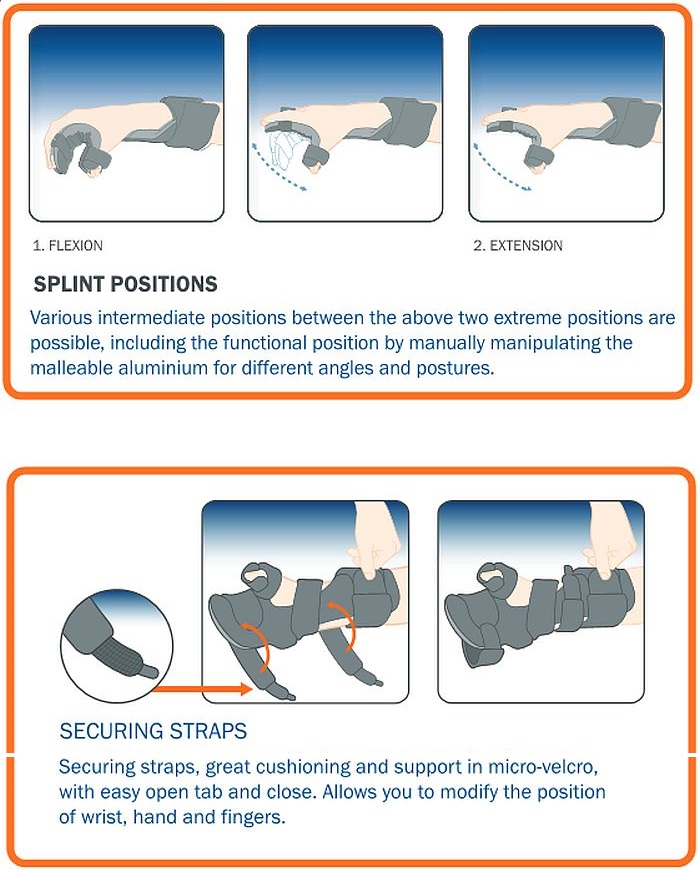
Protect the joints and prevent contractures; Molded in a stationary position with the tissues at maximum length. Turn the forearm back in pronation before the material hardens. Some clinicians refer to this as the position of safe immobilization (posi). The proximal interphalangeal (pip) and distal interphalangeal (dip).
Web one intervention used to treat spasticity is resting hand splints. Immobilize & maintain the hand/joint in one position. Rhs (resting hand splint) reasons for splinting: Turn the forearm back in pronation before the material hardens. Molded in a stationary position with the tissues at maximum length.
Support the wrist and joints of your fingers and thumb in a better position. Start by wearing for 15 minute periods three to four times daily. This book is a basic primer for orthotists and occupational therapists who fabricate splints for the diseased and injured hand. Resting hand splints have many advantages: Wait until the material begins to harden slightly, and mould a cone that lies diagonally and fits snugly in the palm of the hand.
Turn the forearm back in pronation before the material hardens. Place the pattern on the temporarily supinated forearm. Place the forearm in the large trough. Web the thermoplastic material chosen for this orthosis must be rigid enough to support the patient’s limb, but easily molded to contour and drape to the exact anatomy. Position the thumb and mould the material around it. Wait until the material begins to harden slightly, and mould a cone that lies diagonally and fits snugly in the palm of the hand. Rhs (resting hand splint) reasons for splinting: • increase functional range of motion • prevent or decrease muscle tightness • support areas that may need rest or healing care and cleaning: Start by wearing for 15 minute periods three to four times daily. Web resting hand splint to ensure optimal function it is important that the cover is well applied and adjusted correctly in the thumb section (see illustration in circle below). Web there are couple of options of patterns when it comes to making resting splints, but i prefer the “paddle” as i find it gives the thumb a better position and it tends to be a bit stronger. This helps with hand hygiene. Cut the edges straight and round them off. Using the splint you will be shown how to use the splint. The basic anatomy of the hand and the principles of living are.
Web A Resting Hand Split Will Help Your Hands Be In A More Natural Position.
Apply splint starting at thumb,. Support the wrist and joints of your fingers and thumb in correct position. Protect the joints and prevent contractures; Do the same at the proximal end.
From Thumb To 2” From The Antecubital.
Place the pattern on the temporarily supinated forearm. Web your splint has been made to rest the small joints of the hand in a supportive position and help manage any hand pain you are experiencing. Properly position and protect the affected hand; • splint should be washed by hand in warm water using a mild detergent.
Turn The Forearm Back In Pronation Before The Material Hardens.
Can help reduce pain, swelling, and tightness in the wrists and fingers. Ensure that the radial edge of the splint lies diagonally. Cut splint, stretch splint padding over both fiberglass edges, add minimal water, blot. Wait until the material begins to harden slightly, and mould a cone that lies diagonally and fits snugly in the palm of the hand.
Molded In A Stationary Position With The Tissues At Maximum Length.
These splints may be prefabricated or custom made by your therapist. Cut the edges straight and round them off. Web this leaflet is for patients who have been given a resting splint to wear. Resting hand splints have many advantages: