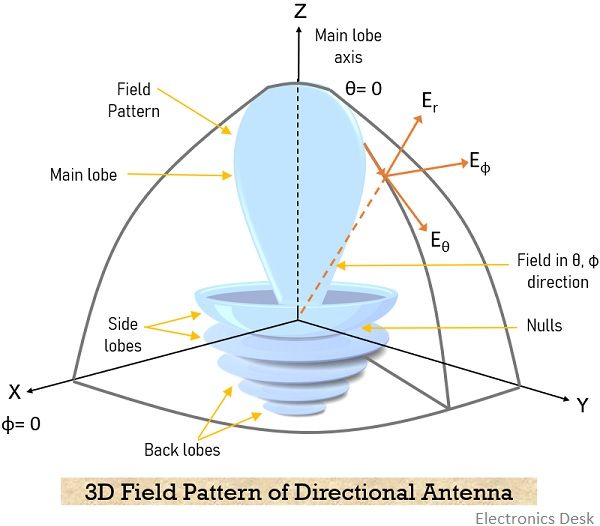
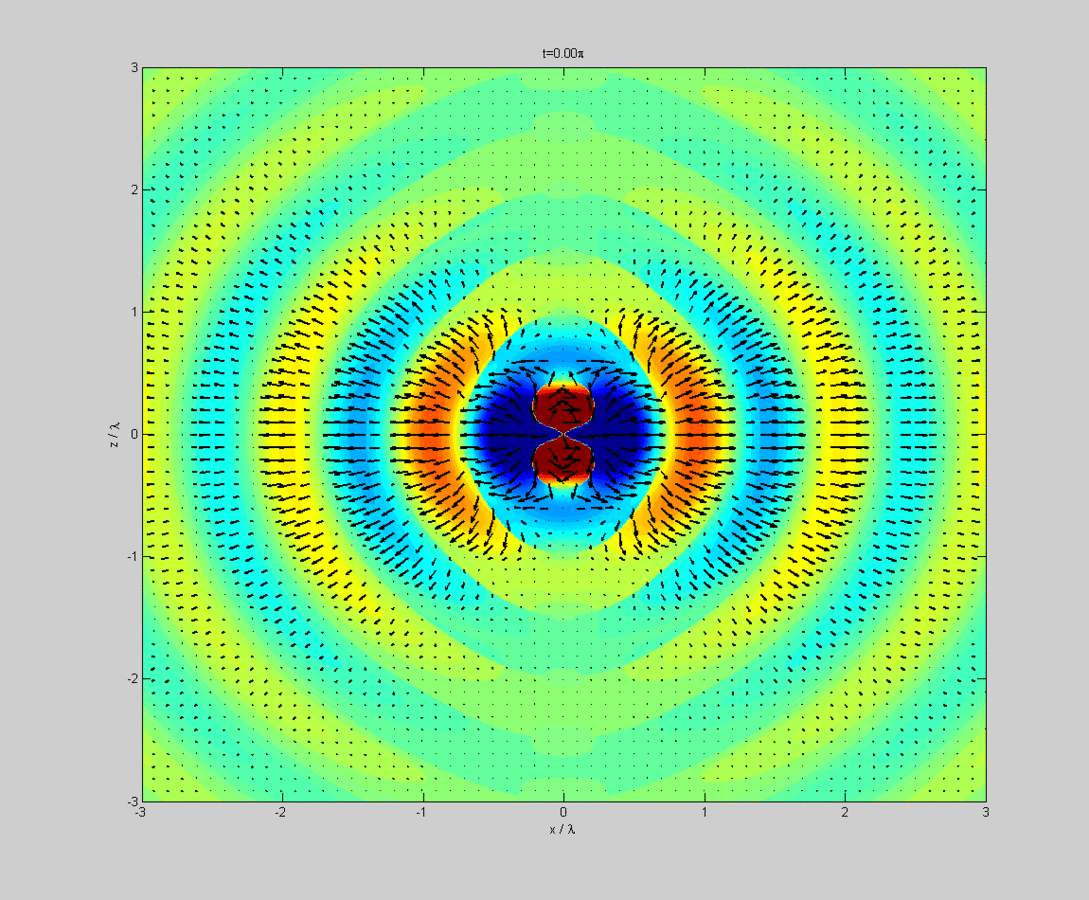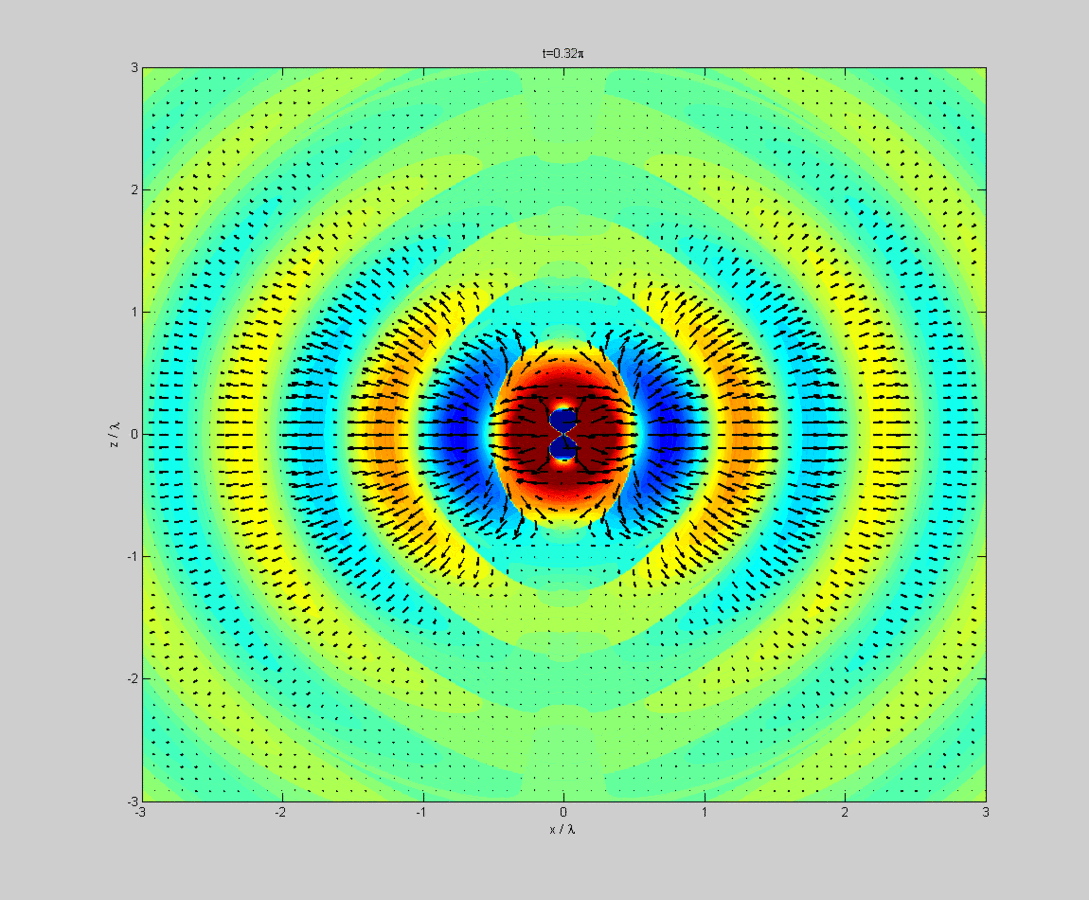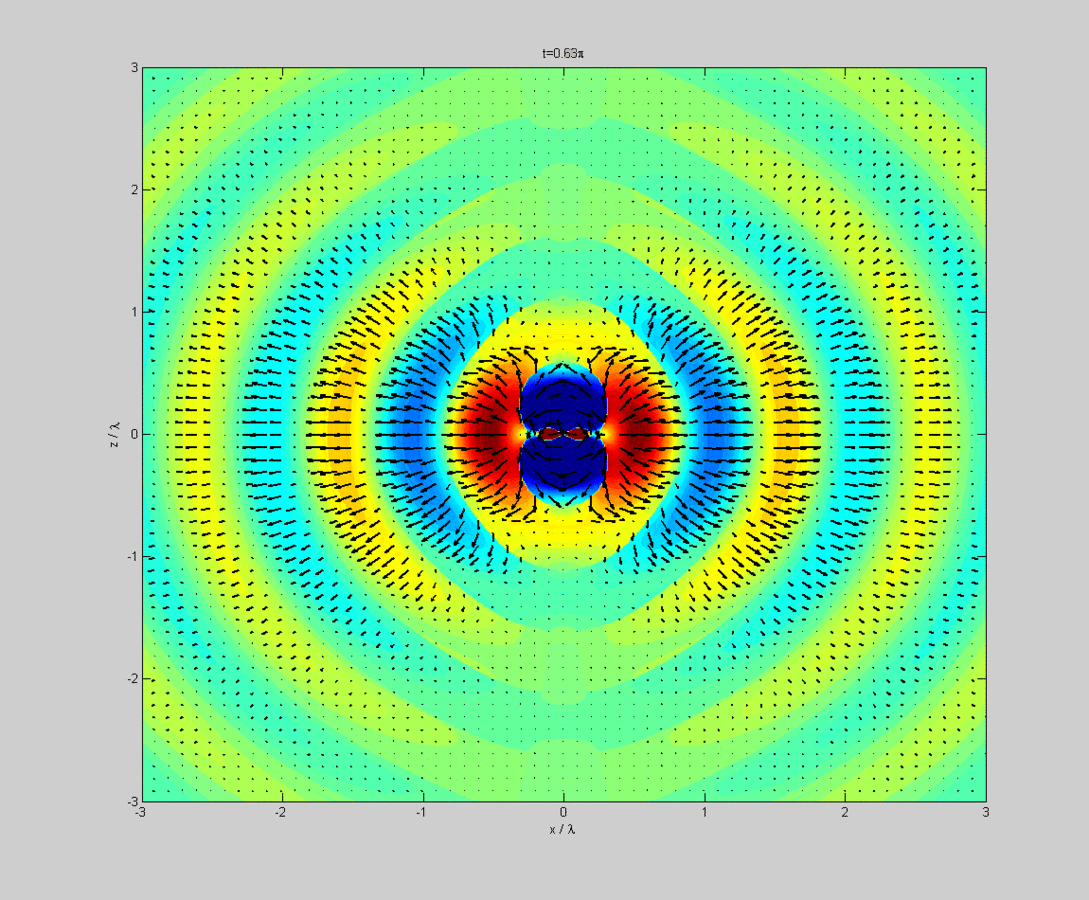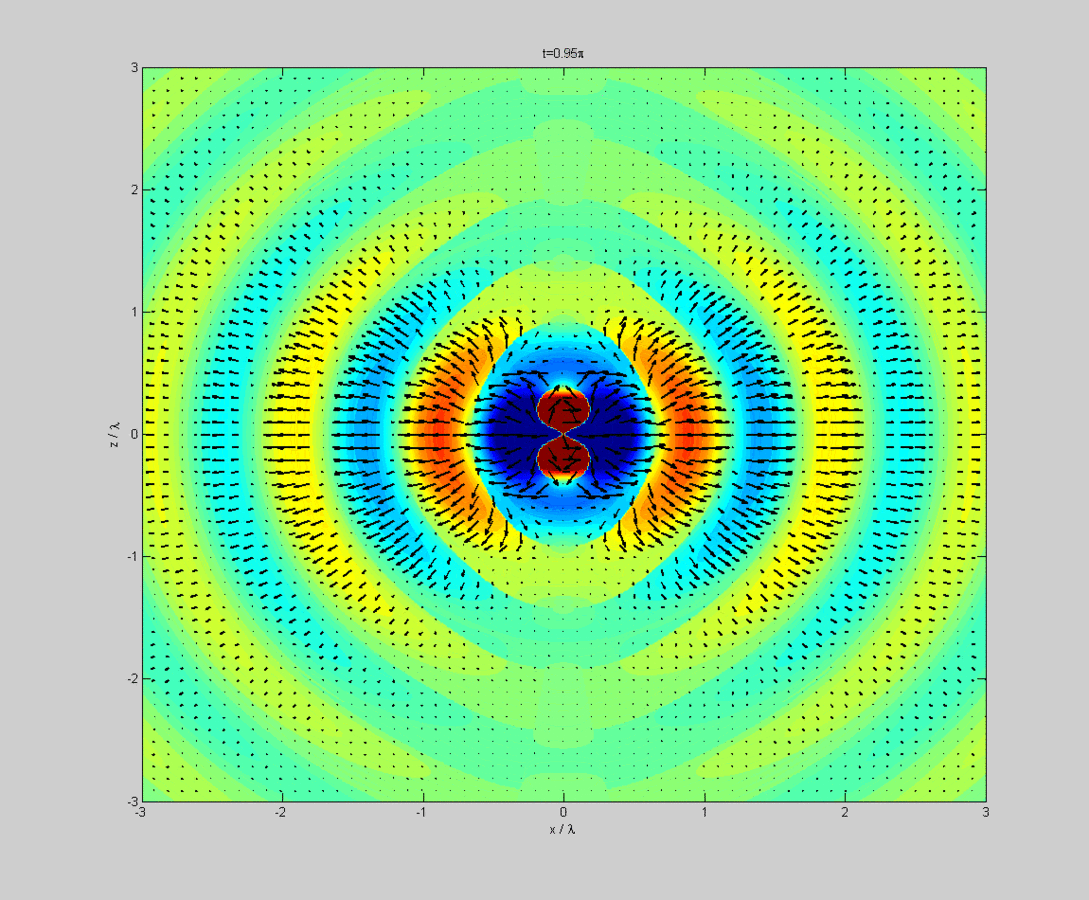
Web gain is a key parameter for antennas that is a product of radiation directivity and electrical efficiency. Note the multiple lobes at varying elevation angles above the horizontal. Consider the radiation pattern given by: It represents the relative intensity of the energy radiation or the amount of the electric or magnetic field strength as a function of the direction to the antenna. This power variation as a function of the arrival angle is observed in the antenna's far field.
Web loop antennas are usually classified as electrically small ( c < λ / 3 ) and electrically large (c ∼ λ ). More simply, the radiation pattern is a trace out that corresponds to the radiation properties of the antenna in space coordinates (i.e., with respect to angle and distance). Web the antenna pattern is usually a graphical representation of the antenna’s directional characteristic. Web the energy radiated by an antenna is represented by the radiation pattern of the antenna. The general idea and necessary steps are indicated.
The first plot below shows a dipole at an elevation of two wavelengths above a standard earth ground model. The radiation pattern or antenna pattern is the graphical representation of the radiation properties of the antenna and how it radiates energy out into space or how it receives energy (reciprocity). Web an antenna is a device that couples currents to electromagnetic waves for purposes of radiation or reception. To better understand antenna gain, antenna designers utilize two dimensional, and three dimensional patterns to aid in proper antenna selection. The small loops of a single turn have small radiation resistance (< 1 ω) usually comparable to their loss resistance.
Web a radiation pattern defines the variation of the power radiated by an antenna as a function of the direction away from the antenna. These concepts can be easily illustrated. Web loop antennas are usually classified as electrically small ( c < λ / 3 ) and electrically large (c ∼ λ ). Antenna radiation patterns help engineers understand the behavior and performance of an antenna. Feeding methods for patch antennas. Here, c denotes the loop’s circumference. Tradeoffs and design parameters of microstrip antennas. The small loops of a single turn have small radiation resistance (< 1 ω) usually comparable to their loss resistance. As we know from sec. The general idea and necessary steps are indicated. On this page, we'll discuss methods and techniques for measuring the polarization of an antenna. Video simulation of transient fields under a microstrip antenna. Note the multiple lobes at varying elevation angles above the horizontal. We have 3d graphs of real antenna radiation patterns, with a discussion on isotropic, omnidirectional and directional radiation patterns. Introduction, parameters and fields of microstrip antennas.
Web Loop Antennas Are Usually Classified As Electrically Small ( C < Λ / 3 ) And Electrically Large (C ∼ Λ ).
Web fundamental to an antenna's radiation pattern is its polarization. The radiation pattern or antenna pattern is the graphical representation of the radiation properties of the antenna and how it radiates energy out into space or how it receives energy (reciprocity). The first plot below shows a dipole at an elevation of two wavelengths above a standard earth ground model. Web the radiation pattern (rp) (or antenna pattern) is the representation of a radiation property of the antenna as a function of the angular coordinates.
Web The Radiation Pattern Is Defined As A Mathematical Function Or A Graphical Representation Of The Far Field (Ie, For R ≫ 2 D2 / Λ, With D Being The Largest Dimension Of The Antenna) Radiation Properties Of The Antenna, As A Function Of The Direction Of Departure Of The Electromagnetic (Em) Wave.
Tradeoffs and design parameters of microstrip antennas. It is unique to an individual antenna and is made up by plotting its far field (normally radiating) radiation as charted coordinates. 12.2, the superposition integrals for the scalar and vector potentials result in both the radiation and near fields. Note the multiple lobes at varying elevation angles above the horizontal.
Web An Antenna Is A Device That Couples Currents To Electromagnetic Waves For Purposes Of Radiation Or Reception.
Web the radiation pattern of a transmitting antenna describes the magnitude and polarization of the field radiated by the antenna as a function of angle relative to the antenna. We have 3d graphs of real antenna radiation patterns, with a discussion on isotropic, omnidirectional and directional radiation patterns. Antennae are designed to transmit and receive electromagnetic waves. More simply, the radiation pattern is a trace out that corresponds to the radiation properties of the antenna in space coordinates (i.e., with respect to angle and distance).
Since Antennas Are Used To Communicate Wirelessly From Long Distances, This Is The Region Of Operation For Most Antennas.
Web the antenna pattern is usually a graphical representation of the antenna’s directional characteristic. The small loops of a single turn have small radiation resistance (< 1 ω) usually comparable to their loss resistance. Radiation patterns are diagrammatical representations of the distribution of radiated energy into space, as a function of direction. As we know from sec.