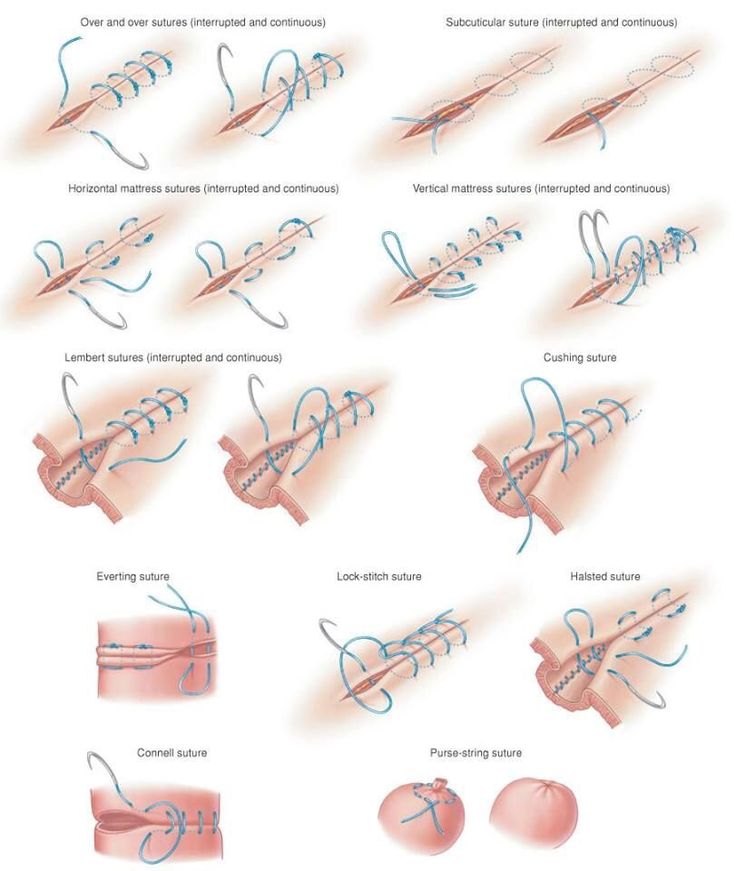
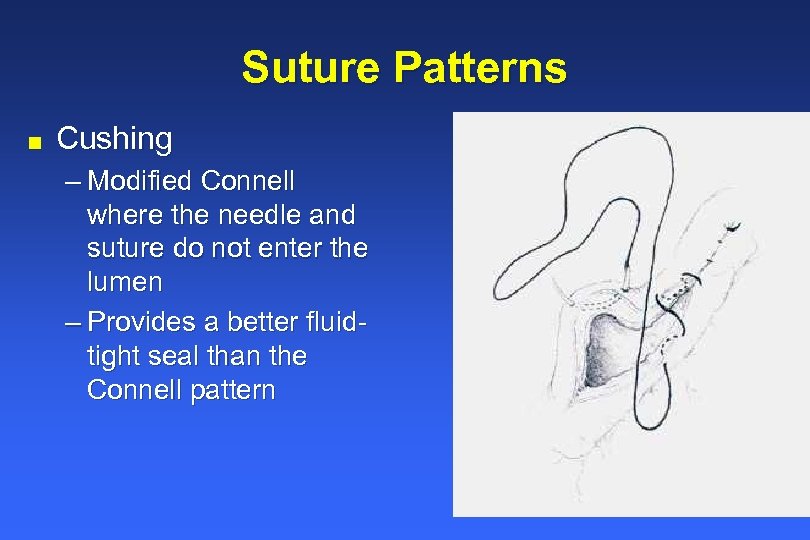
Web with the connell, the needle penetrates the lumen, whereas with the cushing (no ‘l’) it does not (only penetrates serosa, muscularis, and submucosa) the farther the bites are placed from the incision’s edge, the more tissue inverted. Incisions that are farther cranial may penetrate the diaphragm, inadvertently causing a pneumothorax. A type of variation on continuous horizontal mattress sutures. Web the continuous cushing pattern is often used for closing incisions in hollow viscera such as the stomach, urinary bladder and uterus. Retract the abdominal wall with a balfour retractor to expose the cavity, and perform a thorough exploration of the abdominal contents.
This technique is often used to close the incisions in hollow organs such as the stomach, urinary bladder, and uterus. Retract the abdominal wall with a balfour retractor to expose the cavity, and perform a thorough exploration of the abdominal contents. Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues. Web the continuous cushing pattern is often used for closing incisions in hollow viscera such as the stomach, urinary bladder and uterus. Suture patterns can be broadly categorized as interrupted or continuous.
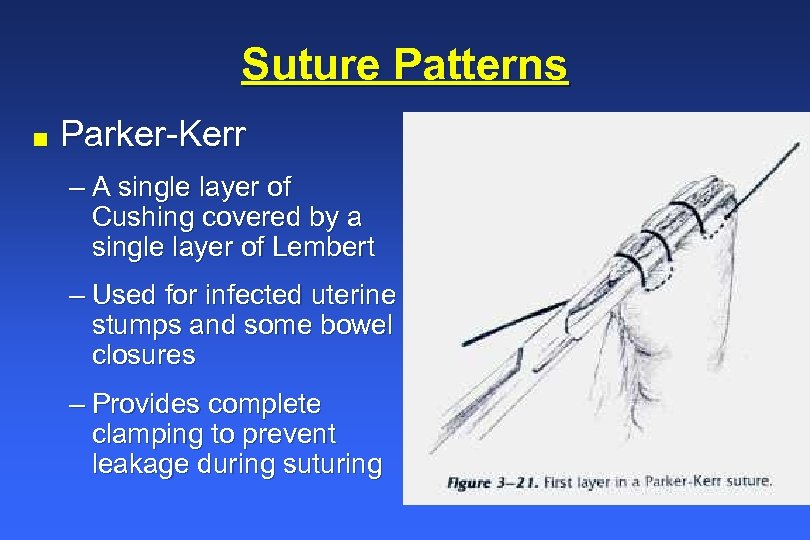
Similar to cushing except for complete penetration into the lumen of the viscera. Web specifically, this curriculum demonstrates five commonly used suturing techniques: It penetrates the submucosa but does not penetrate the organ’s lumen. Make a ventral midline abdominal incision from the xiphoid to the caudal abdomen. Web common suture patterns:
13), should be used because they provide a tight seal, minimize suture exposure,. Web cushing and connell inverted suture pattern demonstration and technique for hollow organs. 4.6 ligatures and suture patterns. This technique is often used to close the incisions in hollow organs such as the stomach, urinary bladder, and uterus. Fast, continuous, easy inverting suture technique for intestinal incision. Web for most tissue closure, appositional suture patterns are preferable, as they allow the best anatomical approximation of the disrupted tissue planes.inverting suture patterns have been traditionally described for the closure of hollow viscera. Web the cushing and connell suture technique is often used to close the incisions in hollow organs such as the stomach, urinary bladder, and uterus. In the cushing suture technique, the suture penetrates into the submucosa without penetrating the organ lumen. Retract the abdominal wall with a balfour retractor to expose the cavity, and perform a thorough exploration of the abdominal contents. The suture penetrates into the submucosa. Michael ross demonstrates the cushing suture pattern and explains the difference between the cushing and connell suture patterns. There isn't a single right way to determine the proper suture pattern for a specific tissue, but helpful guidelines do exist. Make a ventral midline abdominal incision from the xiphoid to the caudal abdomen. Suture patterns can be broadly categorized as interrupted or continuous. Web common suture patterns:
It Runs Parallel To The Incision Line By Taking Tissue Bites On Either Side Of The Incision.
Web with the connell, the needle penetrates the lumen, whereas with the cushing (no ‘l’) it does not (only penetrates serosa, muscularis, and submucosa) the farther the bites are placed from the incision’s edge, the more tissue inverted. Web cushing and connell inverted suture pattern demonstration and technique for hollow organs. Web common suture patterns: Web common suture patterns:
The Suture Penetrates Into The Submucosa And Mucosa.
This technique is often used to close the incisions in hollow organs such as the stomach, urinary bladder, and uterus. Web the continuous cushing pattern is often used for closing incisions in hollow viscera such as the stomach, urinary bladder and uterus. It penetrates the submucosa but does not penetrate the organ’s lumen. It is important to place the suture full thickness to make sure the submucosa is incorporated.
Both The Cushing Suture Pattern And The Connell Suture Technique Are Continuous Sutures, Most Often Used In Hollow Organs Like The Stomach, Uterus, Or Urinary Bladder.
This technique is often used to close the incisions in hollow organs such as the stomach, urinary bladder, and uterus. Incisions that are farther cranial may penetrate the diaphragm, inadvertently causing a pneumothorax. Web inverting patterns turn the cut edges inward and minimize exposed suture. In the cushing suture technique, the suture penetrates into the submucosa without penetrating the organ lumen.
Retract The Abdominal Wall With A Balfour Retractor To Expose The Cavity, And Perform A Thorough Exploration Of The Abdominal Contents.
(ab210) is the code of vertical mattress suture pattern, and (013465)²/3 is the code of cushing suture pattern. Web an overview of the cushing and connell suture patterns. The suture penetrates into the submucosa. Fast, continuous, easy inverting suture technique for intestinal incision bites are taken parallel to the incision but the suture doesn’t pass right through the wall.