However, results are less promising for diagnoses of cri and quadrants of restriction. Web in 2010, the world health organization released benchmarks for training in osteopathy in which they considered cranial osteopathy as an important osteopathic skill. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like physiologic strain patterns, cranial torsion, etiology of torsion and more. Web this particular video is intended as part 3 of a demonstration of the principles of osteopathic cranial manipulative medicine (ocmm) osteopathic manipulative treatment (omt) method diagnosis of. 1 both acute structural damage and subsequent molecular inflammation can result from concussions.
Learn and reinforce your understanding of diagnosing cranial somatic dysfunction. The most prevalent patterns when stratified by the side of dysfunction were right torsion (31%), left sidebending rotation (23%), and left lateral (19%). This information was used to determine whether different physicians observed particular strain patterns in greater frequency between parkinson’s patients and controls. Each strain represent a variation on a theme. 1 both acute structural damage and subsequent molecular inflammation can result from concussions.
Web diagnosing cranial somatic dysfunction videos, flashcards, high yield notes, & practice questions. However, the evidence supporting the reliability of diagnosis and the efficacy of treatment in this field appears scientifically weak and inconsistent. Occiput, sphenoid, ethmoid, vomer, palatine, interpalatine. Web describe the mechanism and direction of forces that may produce cranial strain patterns as a result of trauma (include the following strain patterns: Web concussions are traumatic brain injuries that result from a sudden strike of forces to the cranium.
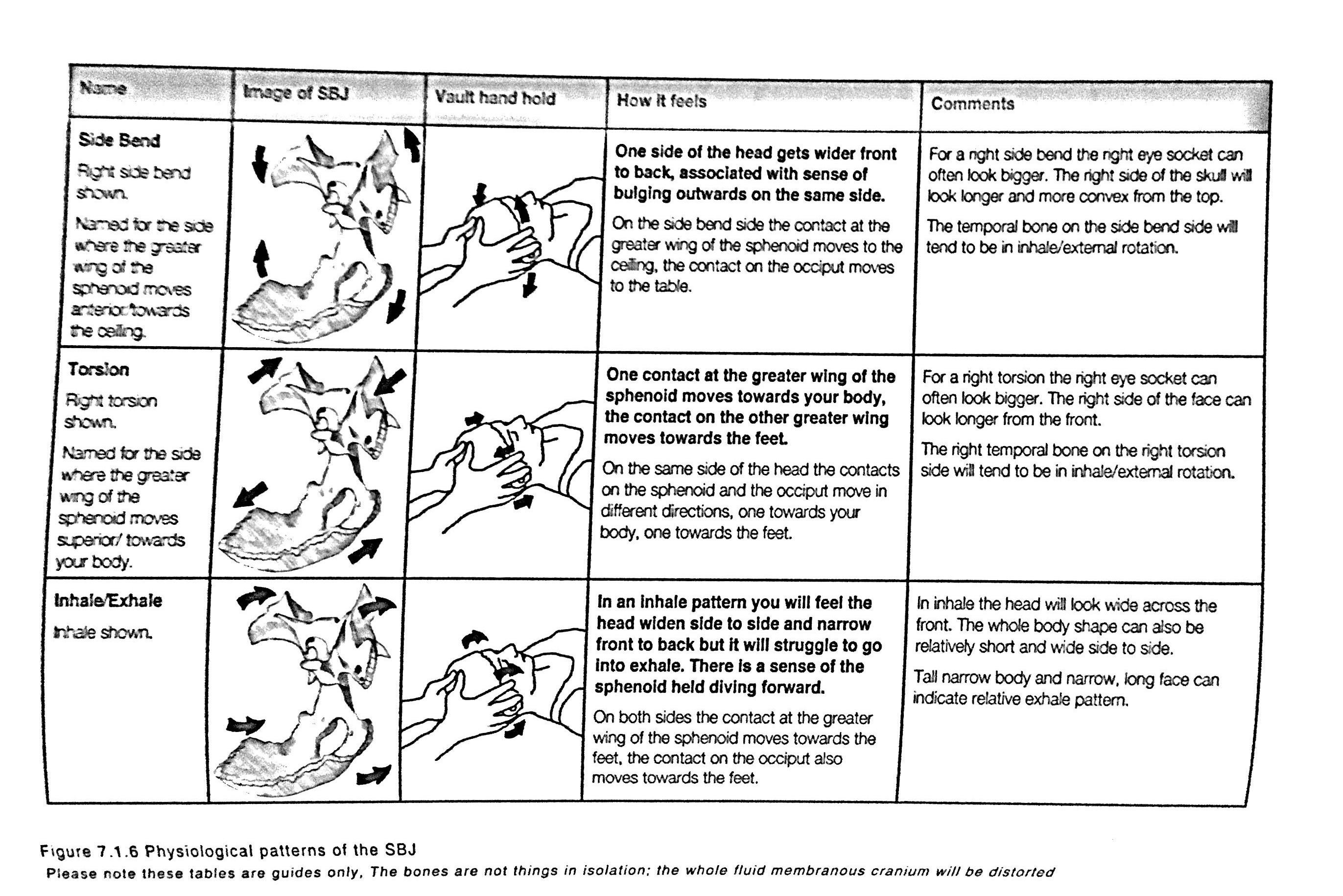
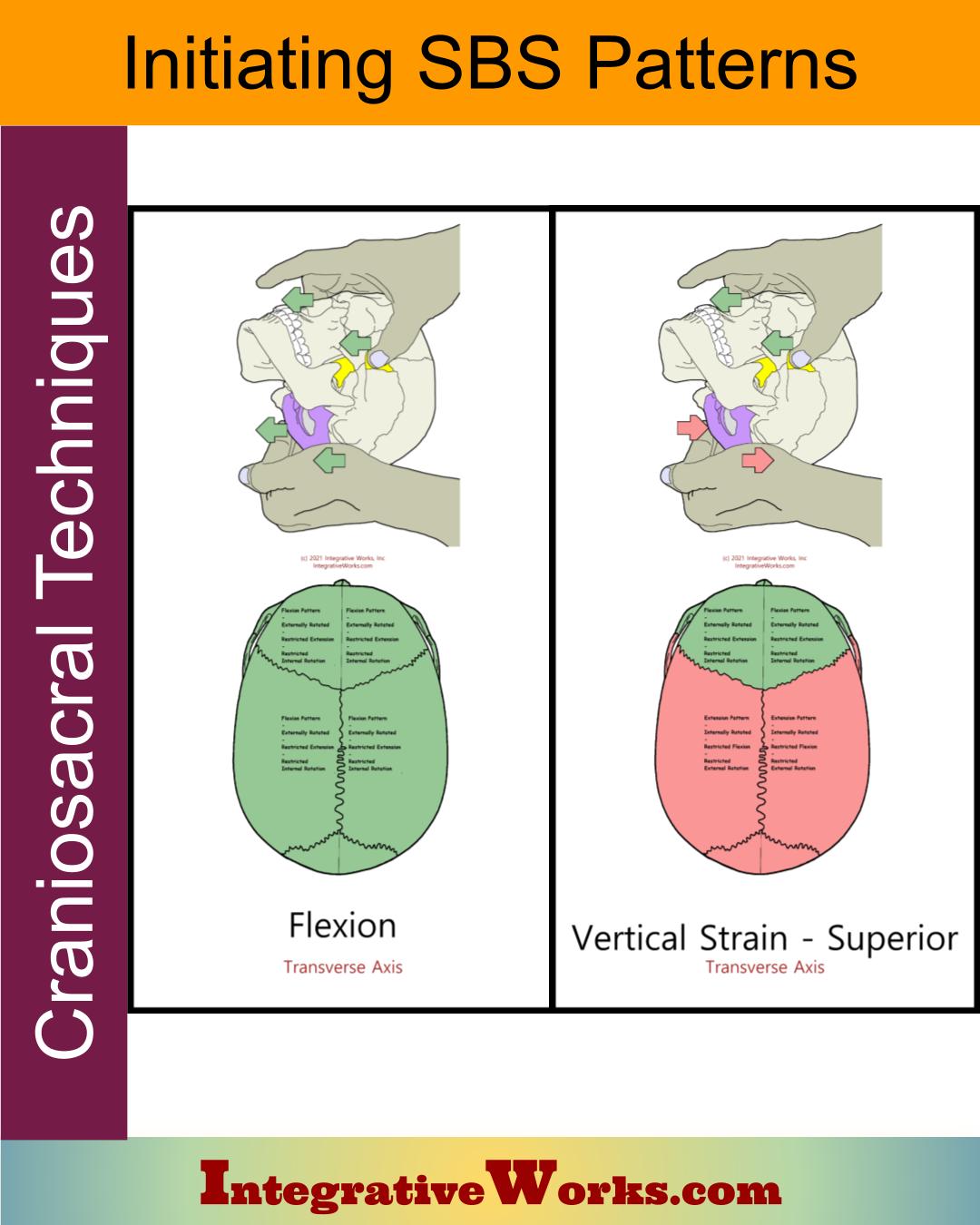
Due to the biomechanical nature of this trauma, cranial somatic dysfunctions may commonly be seen in patients with concussion. Web in 2010, the world health organization released benchmarks for training in osteopathy in which they considered cranial osteopathy as an important osteopathic skill. Strains are named by the motion of the sphenoid and characterized as physiologic or pathologic. Occiput, sphenoid, ethmoid, vomer, palatine, interpalatine. This information was used to determine whether different physicians observed particular strain patterns in greater frequency between parkinson’s patients and controls. Each strain represent a variation on a theme. Web this particular video is intended as part 3 of a demonstration of the principles of osteopathic cranial manipulative medicine (ocmm) osteopathic manipulative treatment (omt) method diagnosis of. Web quiz yourself with questions and answers for opp iv exam 3: Cranial strain patterns, so you can be ready for test day. Superior vertical strain, inferior vertical strain, lateral strain, sbs compression, &. Concussions can cause cognitive impairment, somatic symptoms, and behavioral changes. 1 both acute structural damage and subsequent molecular inflammation can result from concussions. Web reveals unusual presentation of absence of concomitant cranial base strain pattern: In relation to the skull have their own mobility. Web torsion and sidebending rotation were the most common cranial strain patterns observed, comprising 72% of all identified patterns.
The Most Prevalent Patterns When Stratified By The Side Of Dysfunction Were Right Torsion (31%), Left Sidebending Rotation (23%), And Left Lateral (19%).
Web this particular video is intended as part 3 of a demonstration of the principles of osteopathic cranial manipulative medicine (ocmm) osteopathic manipulative treatment (omt) method diagnosis of. This information was used to determine whether different physicians observed particular strain patterns in greater frequency between parkinson's patients and controls. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like cranial flexion: Web lateral strains are a type of nonphysiologic cranial dysfunction in which the sphenoid and occiput rotate around 2 vertical axes that go through the sphenoid and foramen magnum, in the same directions.
Learn And Reinforce Your Understanding Of Diagnosing Cranial Somatic Dysfunction.
A case report. international journal of osteopathic medicine 25 (2017): Symptoms may vary in severity, depending on the degree of traumatic force. Due to the biomechanical nature of this trauma, cranial somatic dysfunctions may commonly be seen in patients with concussion. In osteopathic cranial manipulative medicine, strain patterns are somatic dysfunctions of the sphenobasilar synchondrosis (sbs), occurring when normal physiologic motions of flexion and extension are altered.
Web Randal Davis Explains The Mechanics Of Several Cranial Strain Patterns As Well As How To Work Through Them Using Cranial Hands. The Axis Of Motion For The Strains Are Also Discussed.
Strains are named by the motion of the sphenoid and characterized as physiologic or pathologic. Web concussions are traumatic brain injuries that result from a sudden strike of forces to the cranium. Concussions can cause cognitive impairment, somatic symptoms, and behavioral changes. However, the evidence supporting the reliability of diagnosis and the efficacy of treatment in this field appears scientifically weak and inconsistent.
Left Torsion Rotation About Which Axis And Which Direction How Do Your Hands Move W/ This Diagnosis?
Web quiz yourself with questions and answers for opp iv exam 3: Each strain represent a variation on a theme. Superior vertical strain, inferior vertical strain, lateral strain, sbs compression, &. Web osteopathic physicians can obtain substantial intraobserver reliability when diagnosing cranial strain patterns in healthy subjects as well as those with asthma or headache.