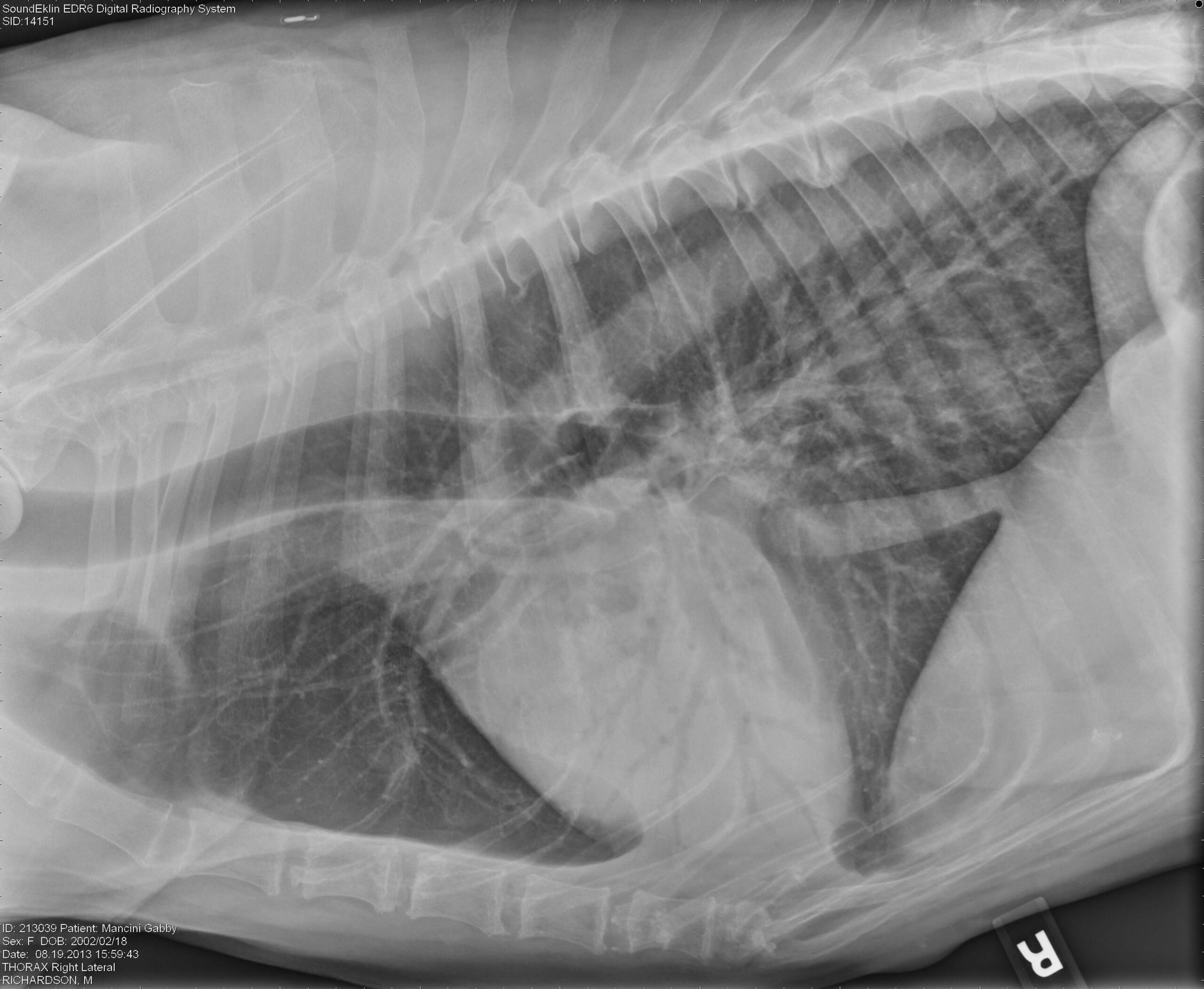
Web to describe the clinical disease, diagnostic findings, medical management, and outcome in dogs with alveolar echinococcosis (ae). Web thoracic radiographs revealed an alveolar pattern in the left cranial and caudal lung lobes, consistent with pneumonia. The silhouette sign (=border effacement) is the hallmark radiographic sign of an alveolar disease. Web diffuse pulmonary disease may be in the form of a bronchial pattern, or interstitial or alveolar pattern. An alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space.
Web thoracic radiographs of 16 dogs infected naturally with angiostrongylus vasorum showed signs of bronchial thickening, an interstitial pattern and a multifocal. Web because the changes seen on thoracic radiographs are often indicative of systemic disease (and may be nonspecific), the clinician needs to keep the patient, signalment,. Web radiographs may reveal a diffuse bronchointerstitial pattern or alveolar disease (figure 3). An alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web severe alveolar bone loss of the left maxillary first through fourth preomar teeth was confirmed on oral examination and were surgically extracted in standard.
Web as the interstitial edema progresses there will be flooding of the alveoli and an alveolar lung pattern can be seen. Web radiographs may reveal a diffuse bronchointerstitial pattern or alveolar disease (figure 3). Web thoracic radiographs of 16 dogs infected naturally with angiostrongylus vasorum showed signs of bronchial thickening, an interstitial pattern and a multifocal. Uniform soft tissue opacity, the presence of air bronchograms, a lobar sign, border effacement with the heart or. Web thoracic radiographs revealed an alveolar pattern in the left cranial and caudal lung lobes, consistent with pneumonia.
Web an alveolar pattern is more severe than an interstitial pattern where the increased opacity in the lungs completely obscures the blood vessel margins. (not all signs seen in every case) 1. Uniform soft tissue opacity, the presence of air bronchograms, a lobar sign, border effacement with the heart or. Web the components of an alveolar pattern include: Radiographic signs of an alveolar pattern include: The silhouette sign (=border effacement) is the hallmark radiographic sign of an alveolar disease. Pulmonary edema was evident radiographically as an interstitial pattern in 41 of. Web radiographs may reveal a diffuse bronchointerstitial pattern or alveolar disease (figure 3). The only distinction these patterns make with. Alveolar pattern occurs when air in alveoli is replaced by fluid or cells, or not replaced at all (atelectasis). Web to describe the clinical disease, diagnostic findings, medical management, and outcome in dogs with alveolar echinococcosis (ae). Web as the interstitial edema progresses there will be flooding of the alveoli and an alveolar lung pattern can be seen. A total collapse of the alveoli. Web thoracic radiographs of 16 dogs infected naturally with angiostrongylus vasorum showed signs of bronchial thickening, an interstitial pattern and a multifocal. An alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space.
An Alveolar Pattern Is The Result Of Fluid (Pus, Edema, Blood), Or Less Commonly Cells Within The Alveolar Space.
Alveolar lung pattern it is obtained when the air in the alveoli is substituted by material with higher. Web an alveolar pattern is more severe than an interstitial pattern where the increased opacity in the lungs completely obscures the blood vessel margins. Web radiologic features consistent with cardiac enlargement were present in all dogs. Web thoracic radiographs revealed an alveolar pattern in the left cranial and caudal lung lobes, consistent with pneumonia.
Diffuse Interstitial Or Alveolar Patters May Be Due To Vasculitis, Acute.
(not all signs seen in every case) 1. Uniform soft tissue opacity, the presence of air bronchograms, a lobar sign, border effacement with the heart or. Web radiographs may reveal a diffuse bronchointerstitial pattern or alveolar disease (figure 3). Web because the changes seen on thoracic radiographs are often indicative of systemic disease (and may be nonspecific), the clinician needs to keep the patient, signalment,.
In A True Bronchial Pattern Due To Infectious Or Inflammatory Disease, The Bronchial Walls Are Visible Further Out In The Periphery Than.
The only distinction these patterns make with. The patient was hospitalized for supportive care and. An alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web an alveolar lung pattern is an opaque lung that completely obscures the margins of the pulmonary blood vessels.
Web The Components Of An Alveolar Pattern Include:
In dogs with chronic endocardiosis that acutely. Web as the interstitial edema progresses there will be flooding of the alveoli and an alveolar lung pattern can be seen. Uniform, homogeneous fluid opacity, varying from faint or fluffy, to solid, complete opacification 2. Patients with eb have airway cytology supportive of eosinophilic inflammation and.